How is an anal fissure treated?
The goal of treatment is to reduce pressure in the anal canal by softening the stool and alleviating discomfort and bleeding. Conservative treatments are tried first and include one or more of the following:
- Preventing constipation through the use of laxatives, increasing fluid intake while avoiding caffeine-containing products (which cause dehydration), and dietary adjustments (increasing the intake of fiber-rich foods and fiber supplements)
- Sitz baths in warm water for 10 to 20 minutes several times a day to promote relaxation of the anal muscles
- Gentle cleansing of the anal area
- Avoiding straining or prolonged sitting on the toilet
- Using petroleum jelly to lubricate the anal area
The conservative practices mentioned above heal the fissure (80 to 90 percent) within several weeks to a few months. However, when treatments fail and the fissure persists or recurs, other measures should be tried, including:
- Using hydrocortisone suppositories, foams, or creams to reduce inflammation
- Applying other creams and ointments with muscle relaxant properties (to relax the anal muscles), anesthetic ointments (to reduce pain if pain is related to bowel movements), nitroglycerin ointments, or calcium channel blockers (to relax the anal muscles and increase blood flow to the area, promoting healing)
- Injection of botulinum toxin A (Botox) into the anal sphincter. The injection temporarily paralyzes the anal sphincter muscle, resulting in pain relief and promoting healing.
Surgical Treatment
What does the surgical approach involve?
Before surgery, your doctor will reassess you and may conduct other tests to determine why other treatments have failed to heal the fissure.
Some of the reasons a fissure may fail to heal include scarring or muscle spasms of the internal anal sphincter muscle. Surgery usually involves making an incision in a small section of the internal anal sphincter. This reduces pain and spasms, allowing the fissure to heal. The incision made in the muscle rarely results in a loss of bowel control. Surgery can usually be performed on an outpatient basis. Pain is relieved after a few days, and complete healing occurs within a few weeks.
Is there anything I can do to prevent an anal fissure?
For fissures in infants:
- Change diapers frequently and treat constipation (if this is deemed the cause).
For fissures in infants:
- Keep the anal area dry
- Wipe the area with soft materials, a wet cloth, or cotton, avoiding rough and scented toilet paper
- Address constipation and diarrhea promptly
- Avoid irritation to the anal area
 What is an anal fissure?
What is an anal fissure?
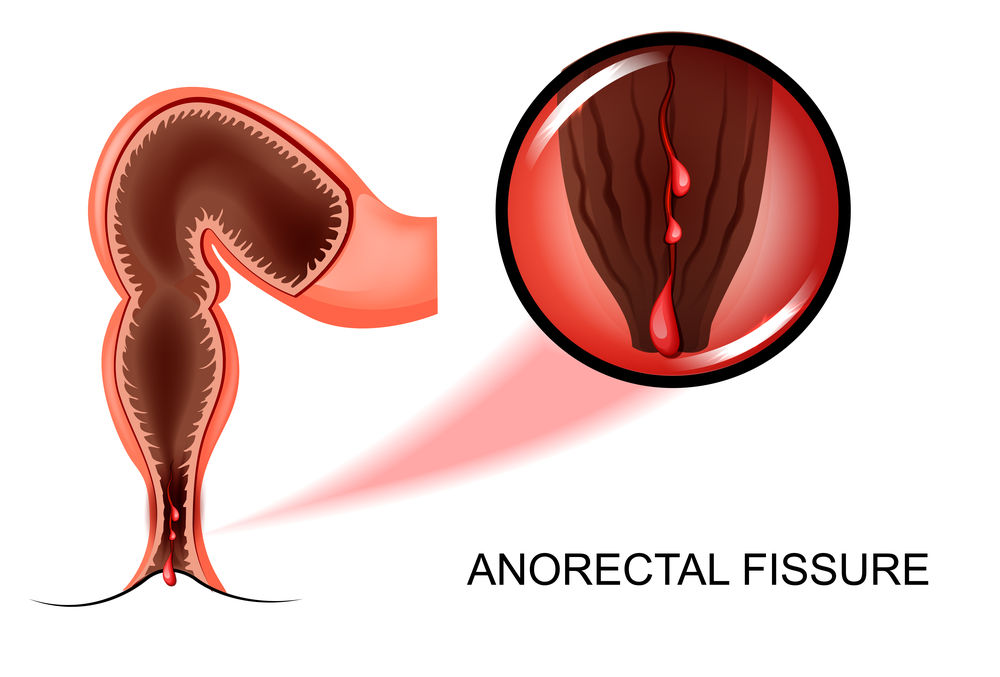 What is an anal fissure?
What is an anal fissure?